Systolic and Diastolic BP Control in Metabolic Syndrome Patients with Metadichol® a Novel Nano Emulsion Lipid-Juniper Publishers
JUNIPER PUBLISHERS-OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL OF CARDIOLOGY & CARDIOVASCULAR THERAPY
Abstract
Metadichol®, [1] a nano formulation a mixture of long
chain alcohols that is present in many foods like rice and sugar cane
and is derived from the waste of the sugar cane industry. It is a
renewable resource. Most of the clinical data in literature is a:
non-nano formulation either a tablet or capsule which have not shown any
efficacy.
Given its safety profile, we carried out a small
open-label pilot study on diabetic patients with hypertension who had in
additional co-morbidities such as dyslipidemia, obesity, and
hypertension. None of them were on any hypertensive medication.
Our studies on patients for 60 weeks in an open-label
study @20mg per day showed that it is possible to bring about
improvements in Systolic and diastolic pressure in addition to CRP,
VLDL, HDL, Triglycerides and waist circumference reduction and reduction
in insulin resistance. Interestingly Vitamin C levels doubled. The
study showed a vast improvement over existing therapies and with no side
effects minor or major to report.
Introduction
It is paradoxical that despite the enormous advances
in antihypertensive drug therapy, the Number of people with uncontrolled
hypertension has continued to rise. A new 2017 study [2] by the
American Heart Association, projects that by 2035, cardiovascular
disease (CVD), will become the most expensive and prevalent killer if
left unchecked, will place a crushing economic and health burden on the
nation’s financial and health care systems. According to the study, in
the next two decades, the number of Americans with CVD will rise to
131.2 million-45 percent of the total U.S. population with costs
expected to reach $1.1 trillion. There are many hypertensive drugs, but
prolonged use and multi-drug use does lead over time to side effects.
There is a need for a safe, cheap alternative to existing drugs.
Metadichol is a Nanoemulsion of long-chain lipid alcohols (C-26, C-28,
and C-30), which are commonly known as Policosanols. and it binds to VDR
and which has been shown to have a role in hypertension [1,3-5].
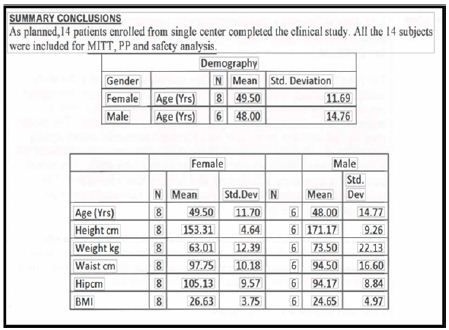
Fourteen patients were enrolled in Nonrandomized,
Open, Single-group, study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of
Metadichol in subjects with metabolic syndrome at a hospital in
Bangalore, India. The dosage was 20mg per day. Most of the patients were
on antidiabetic medication Metformin and Glucophage in addition. None
of the patients were on hypertensive medication.
The study population consisted of male or
non-pregnant female patients aged 18 years of age with a previously
diagnosed various medical conditions. All patients provided written
informed consent to participate in the study before being screened.
The patient information sheet detailed the procedures
involved in the survey (aims, methodology, potential risks,anticipated
benefits) and the investigator explained these to each
patient. The patient signed the consent form to indicate that the
information had been disclosed and understood. The patient was
then allowed time to consider the information presented before
signing and dating the informed consent form to indicate that
they fully understood the information, and willingly volunteered
to participate in the study. The patient was given a copy of the
informed consent form for their information. The original copy
of the informed consent was kept in a confidential file in the
Investigators center records.
Criteria for exclusion from the study included pregnant
or lactating females any serious and uncontrolled medical
conditions interfering with the study or placing the patient at
unacceptable risk. Only patients who fulfilled all the inclusion
criteria and did not meet any of the exclusion criteria were
enrolled into the study.
Metadichol was well tolerated which was confirmed by no
incidences of adverse events and good compliance. Vital signs
were all within the normal range during the study. There were
no clinically significant abnormal findings at any of the visits
in the treatment groups. Physical examination was found to
be normal during the study for all the subjects. There were no
clinically significant abnormal findings at any of the visits.
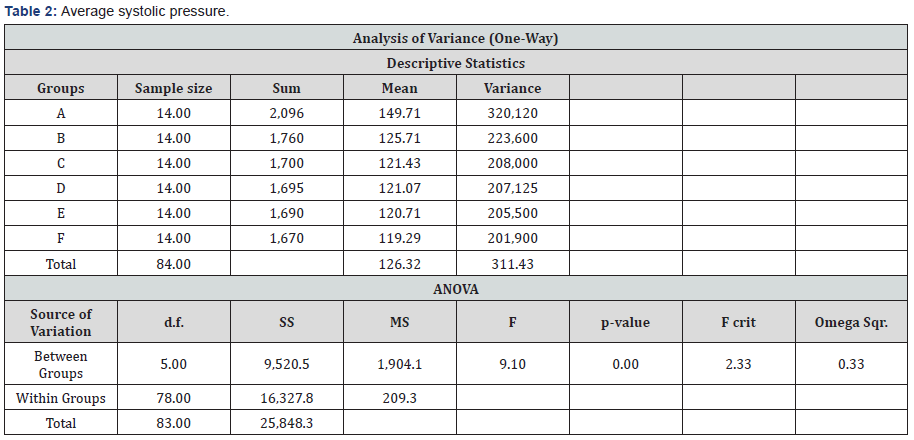
Analysis of Variance one way was carried out using JMP
software from SAS showed that the following biomarkers were
significant <0.05 even in the absence of controls. These were:
- Systolic and diastolic pressure
- hS-CRP (high sensitivity C-reactive protein)
- Experimental VLDL
- Vitamin C
- A/G ratio and Globulins
- Triglyceride/HDL ratios
- e-GFR a biomarker of kidney function.
The key biomarkers that are the subject of this
communication are Systolic, diastolic CRP, VLDL as well as A/G
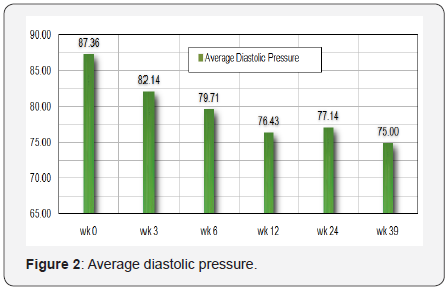
ratios and Globulin. Table 1, Figures 1 & 2 and Table 2& 3 show
changes with descriptive statistics for Systolic and diastolic
pressures. The most striking result was the normalization of
blood pressure in 3 weeks.



Nesri et al. [6] found that weekly vitamin D supplementation
50,000i units for 12 weeks had the beneficial effect on the level
of blood pressure in type 2 diabetic patients. Another recent
study [7] also showed a use of 2000 IU Vitamin D showed the
drop of 10mm Systolic and 6mm diastolic. Given that Metadichol
binds to Vitamin D the results are not surprising. The effects go
beyond that. Even more remarkable is its effects on lipids VLDL
and also inflammation markers CRP and increase in Vitamin C
levels. Lieffard et al. [8] showed that higher levels of Vitamin D
are associated with lower levels of C-reactive protein.
Metadichol binds to the vitamin D receptor (VDR) as an
inverse agonist. It is the only known inverse agonist of VDR
known today. Calcitriol (1,25-Dihydroxy Vitamin D) is the
natural ligand for the VDR and acts as an agonist. Metadichol acts
an inverse agonist but more likely is a Protean agonist. Protean
agonists act as both positive and negative agonists on the same
receptor depending on the degree of constitutive activity that
is present. If there is no constitutive activity, the agonist would
be an active agonist. When constitutive activity is present, the
Protean agonist would be an inverse agonist [9]. In addition
to VDR binding, Metadichol shares cross-reactivity with other
nuclear receptors, like PPAR gamma [10], which may explain its
activity against a broad range of biomarkers.
Even more striking is that Vitamin C levels doubled. It is
well known that our ancestors had a functioning gene GULO
that converted glucose into Vitamin C [11]. Humans once madevitamin C in their liver by the production of four enzymes
which convert circulating sugars into ascorbic acid (vitamin
C). Humans today only make 3 of the four enzymes required
to convert glucose (sugar) into Ascorbic acid. A progressive
mutation at some time in past generations deactivated the
gene for the enzyme gluconolactone oxidase and slowly as the
mutation progressed the synthesis of vitamin C came to an end
in humans. The human need for Vitamin C being fulfiiled by
exogenous sources today. This has led to inactivity of the enzyme
L-gulonolactone [12].
Mammals who make their vitamin C can live 8-10 times
beyond their age of physical maturity. Mammals without this
ability have a difficult time reaching 3-4 times. Researchers
believe the reinstallation of the guano-lactone oxidase enzyme
in humans would extend the lifespan of humans [13,14].
A study over a 12-16-year period showed that males with
the highest blood serum levels of vitamin C experienced a 57
percent drop in their risk of dying from any cause compared to
males with low circulating levels of vitamin C [15]. Among men
and women ages 45-79 years, just a 50 milligram increase in
vitamin C consumption was enough to reduce the relative allcause
mortality rate by 20 percent [16].
Another study published in 2001 also confirms a 25-29
percent decreased all-cause mortality rate among adults with
normal to high circulating levels of vitamin C [17].
Since vitamin C is an antioxidant and reduces C-reactive
protein (CRP)-a substance that can support the progression of
CVD [18]. In fact, in a study of active and passive smokers, vitamin
C supplementation (515mg daily) resulted in a 24-percent
reduction in plasma CRP. Ascorbate stimulates the immune
system and can help those with impaired immunity [19,20]. Low
serum 25(OH)D levels are associated with significantly higher
very low density lipoproteins [21].
Today’s approach in drug research is a lock and key, with a
drug acting as a selective ‘key’ that fits into the ‘lock’ of a specific
drug target. Given the many side effects of drugs and to overcome
it the search for high selective ligands has been the approach
of the drug discovery community. This has not delivered any
tangible benefits. Many useful drugs act via modulation of
multiple proteins rather than single targets. Anti-psychotic
drugs commonly exhibit a broad spectrum of activities across
entire families of serotonin and dopamine receptors. Protein
kinase inhibitors like Sutent and Gleevec, have demonstrated
that their anticancer effects are most likely due to their action
on multiple signaling kinases [22].Yıldırım et al. [23] suggested that there are many
keys for
each lock is more common than one key to open many locks.
Their hypothesis based on available data of drug action using
network biology provided insights into how we can improve
drug discovery for complex diseases. Medicines for many disease
states may require multiple activities to be efficacious, together with
the observation that perturbed biological networks is more
important than individual targets. Such an approach has been
highlighted and advocated by Andrew Hopkins [24].
Effective drugs act via modulation of multiple proteins
rather than single targets. Metadichol does just that. It seems to
be operate by optimizing multiple activities, and balancing druglike
properties and eliminating undesirable off target effects.
The inverse/protean activity exhibited by Metadichol leads to it
acting on more than one target, VDR, PPAR gamma as well as
inhibition of cytokines like TNF-alpha, MCP-1, PAI-1 and also the
endogenous increase of Vitamin C levels which we have shown
in our Rat studies [1]. Given the range and breadth of actions of
Metadichol the results suggest that it mimics the effects of 1,25,
dihydroxy Vitamin D3 but without the toxic effect secondary to
calcemia which limits its use as a pharmaceutical agent [25].
Metadichol is the first example of a smart molecule that can
simultaneously modulate multiple targets which could pave
the way to successful treatment of many of these challenging
diseases [26-31].
For more articles in Open Access Journal of
Cardiology & Cardiovascular Therapy please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/jocct/index.php



Comments
Post a Comment